Consumers’ access to multiple food stores varied across the United States
- by Alana Rhone and David Marquardt
- 6/12/2025
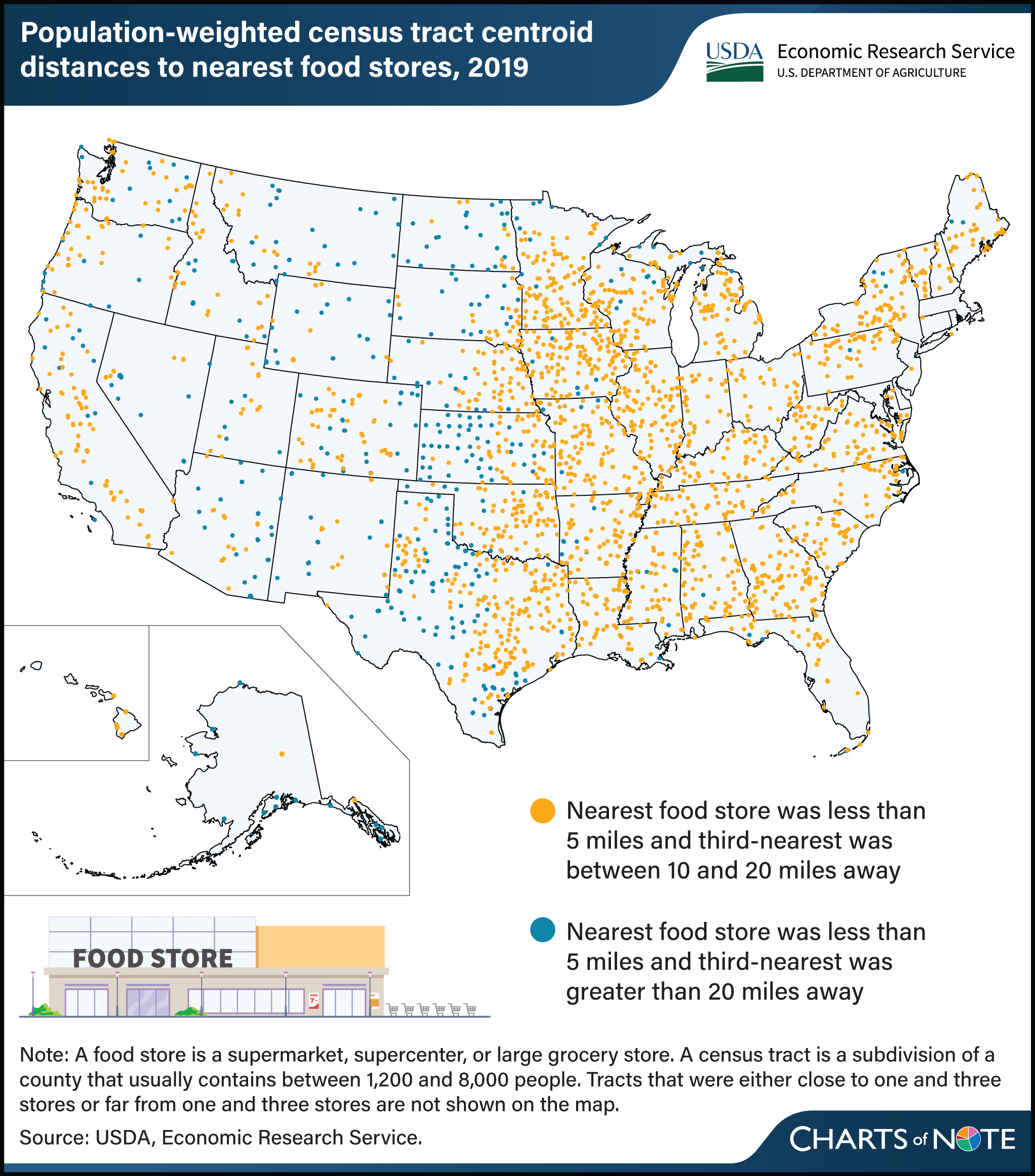
Distance from a person’s home to the nearest food store (supermarket, supercenter, or large grocery store) is one way to measure the ease of access to a major source of a variety of healthy foods. However, a food store with no nearby competitors may not offer the best price, quality, or selection of products. Researchers at USDA, Economic Research Service (ERS) used a variety of data sets to calculate distances between households’ residences and the nearest and third-nearest food stores, addressing both food store access and competition. Evaluating only one food store’s distance may not accurately indicate competitiveness for consumers, as areas near a single store might still face food access limitations compared to those with multiple options. In 2019, 3.08 percent of census tracts were close (less than 5 miles) to one store and also relatively far (10−20 miles) from a third store and 0.63 percent of census tracts were close to one store but far (more than 20 miles) from a third store. In these census tracts, households may have had relatively easy access to one store (less than 5 miles) but may have had less choice in stores because the third-nearest store was far away. Many census tracts were either close to one and three stores or far from one and three stores. Census tracts where the population-weighted center of the tract was within 5 miles of the nearest food store and between 10 and 20 miles from the third-nearest food store were concentrated in the Midwest and portions of the eastern half of the United States. The majority of census tracts in which the population-weighted center was within 5 miles of the nearest food store, but more than 20 miles from the third-nearest food store were mostly concentrated in portions of the Great Plains section of the Midwest and the Southwest. Less competition in the Great Plains and South may be attributed to the rural nature of these areas. This chart updates information in the ERS Amber Waves article U.S. Shoppers’ Access to Multiple Stores Varies by Region using the latest data from the Food Access Research Atlas data product.


