Direct metering of water deliveries most common among large irrigation organizations
- by R. Aaron Hrozencik
- 4/14/2025
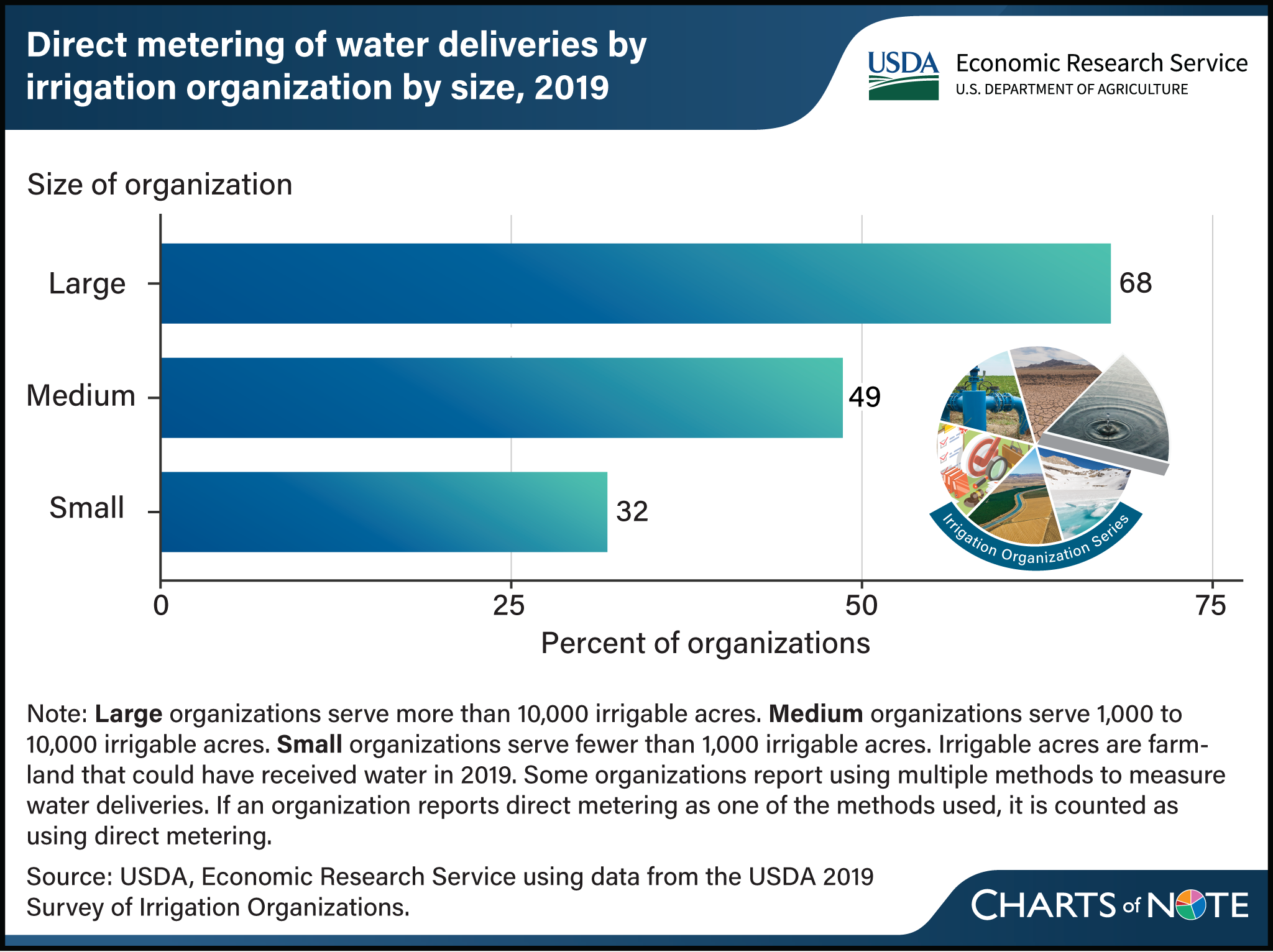
Irrigation organizations use networks of diversion structures, reservoirs, canals, ditches, and pipelines to deliver millions of acre feet of water to their constituents. Accurate and timely measurement of this water allows organizations to track how it is allocated and identify where losses occur, often measuring flows into, within, and out of their systems. The most accurate method of measuring water deliveries is direct metering, although other less accurate methods of measuring, such as self-reporting by constituents or estimates based on delivery time spans, are also common. Sixty-eight percent of large irrigation organizations (those serving more than 10,000 irrigable acres) reported using direct metering to measure water deliveries. Forty-nine percent of medium organizations (serving 1,000 to 10,000 acres) reported using direct metering, and 32 percent of small organizations (serving fewer than 1,000 acres) reported using direct metering to measure water deliveries. This chart was drawn from the USDA, Economic Research Service report Irrigation Organizations: Water Measurement and Pricing, published in February 2025.

