Costs of major foodborne illnesses in the United States increased to $17.6 billion in 2018
- by Sandra Hoffmann
- 6/21/2021
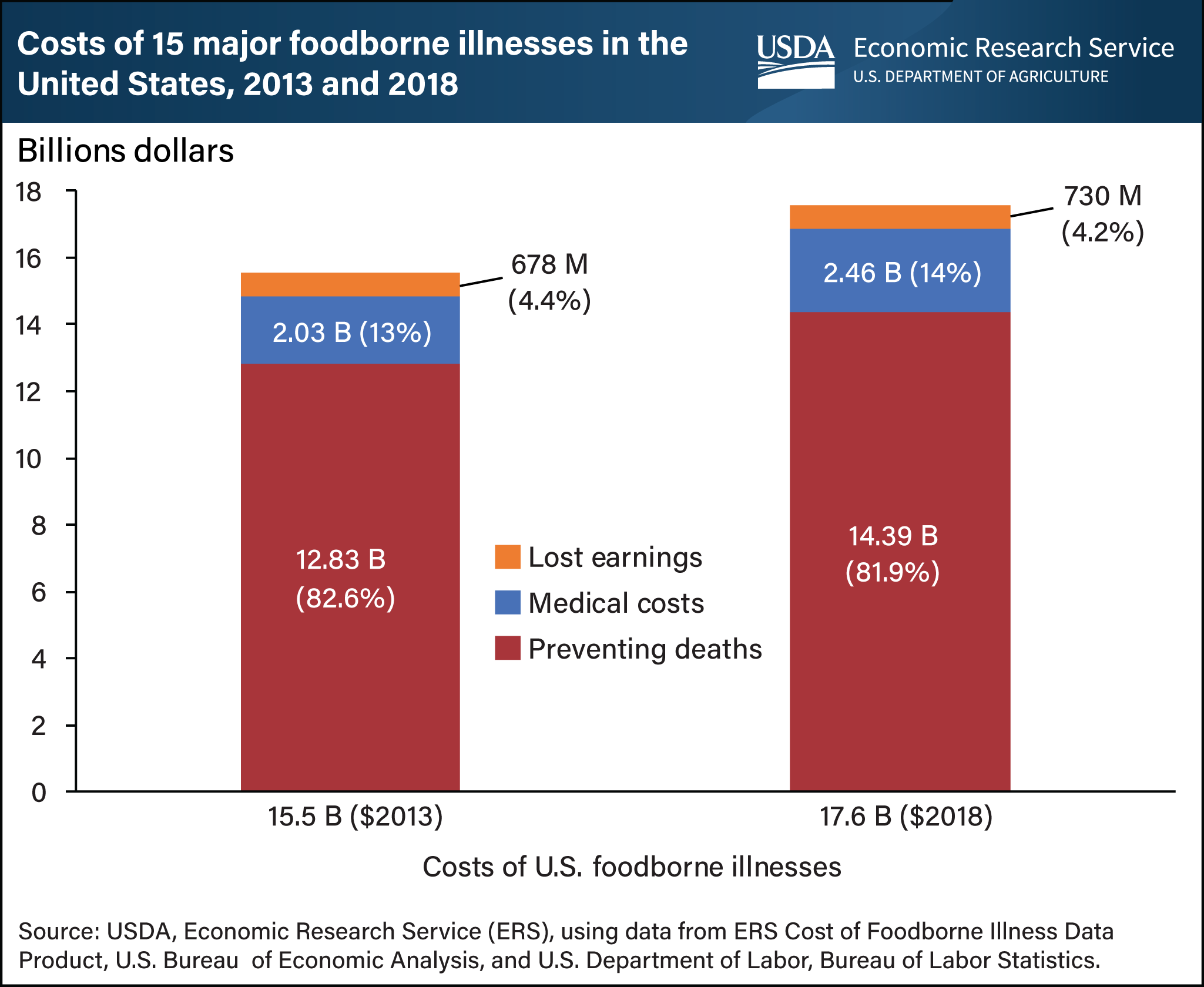
The USDA, Economic Research Service (ERS) estimates that inflation and income growth drove up the costs resulting from 15 foodborne illnesses in the United States by $2 billion from $15.5 billion in 2013 to $17.6 billion in 2018. For this estimate, ERS included medical care costs, the value of lost earnings, and a monetary measure of death based on individuals' willingness to pay to reduce the risk of dying from foodborne illness. The biggest factor behind the increase in the overall costs of foodborne illnesses was the effect of inflation and income growth on the value people place on preventing deaths. However, the value of prevented deaths as a share of overall costs decreased slightly in 2018 compared to 2013 due to the substantial inflation in medical costs. Health effects from foodborne illness can vary by pathogen (bacteria, viruses, and parasites), ranging from a few days of diarrhea to more serious outcomes, such as kidney failure, cognitive impairment, and even death. Determining the overall costs of these health effects provides a common metric to compare impacts of different pathogens, a way to aggregate impacts across illnesses, and a means of comparing the costs of experiencing those illnesses with the costs of preventing them. More information can be found in the ERS’s updated Cost Estimates of Foodborne Illnesses data product. This chart appears in the ERS’s Amber Waves article, “Economic Cost of Major Foodborne Illnesses Increased $2 Billion From 2013 to 2018,” April 2021.

