The United States is the second largest supplier of beef to Japan
- by Andrew Muhammad
- 5/10/2016
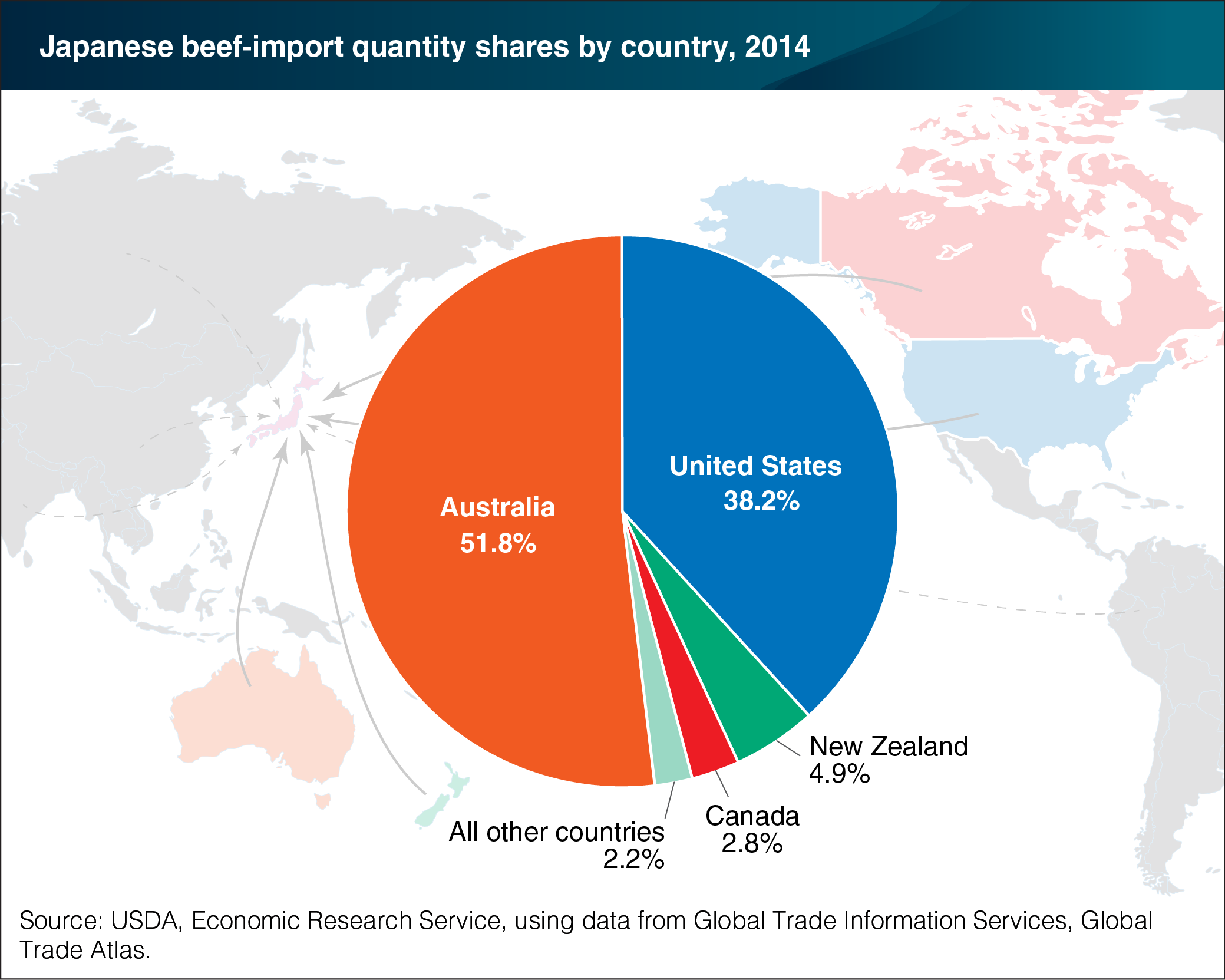
With its large population and limited space for agricultural land, Japan has long been one of the world’s largest importers of food products, including beef. In 2014, Japan imported nearly $3.5 billion of beef and beef products, making it the third largest beef importer in the world. The primary suppliers of these imports are the United States and Australia, which together represented roughly 90 percent of Japan’s 2014 beef imports in terms of both quantity and value. Australia has the larger share, with 51.8 percent of the total quantity of beef and beef-offal products imports and 46.8 percent of the value. The U.S. share of this market, at 38.2 percent of quantity and 43.6 percent of value in 2014, has steadily recovered since 2004-06, when Japan banned imports of most U.S. beef in response to the discovery of bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE) in the United States. The Japan-Australia Economic Partnership Agreement (JAEPA), signed in 2014, significantly reduces tariffs on imports of Australian beef, potentially giving Australia a strong advantage in supplying this market. However, both Australia and the United States are a part of the recently concluded Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP) agreements, which if ratified, could improve U.S. access to this valuable market and lead to higher exports of U.S. beef to Japan. This chart is from the January 2016 report, Tariff Reforms and the Competiveness of U.S. Beef in Japan.


