Farms with higher sales had a larger share of households with positive farm income
- by Anil K. Giri and Christine Whitt
- 6/23/2021
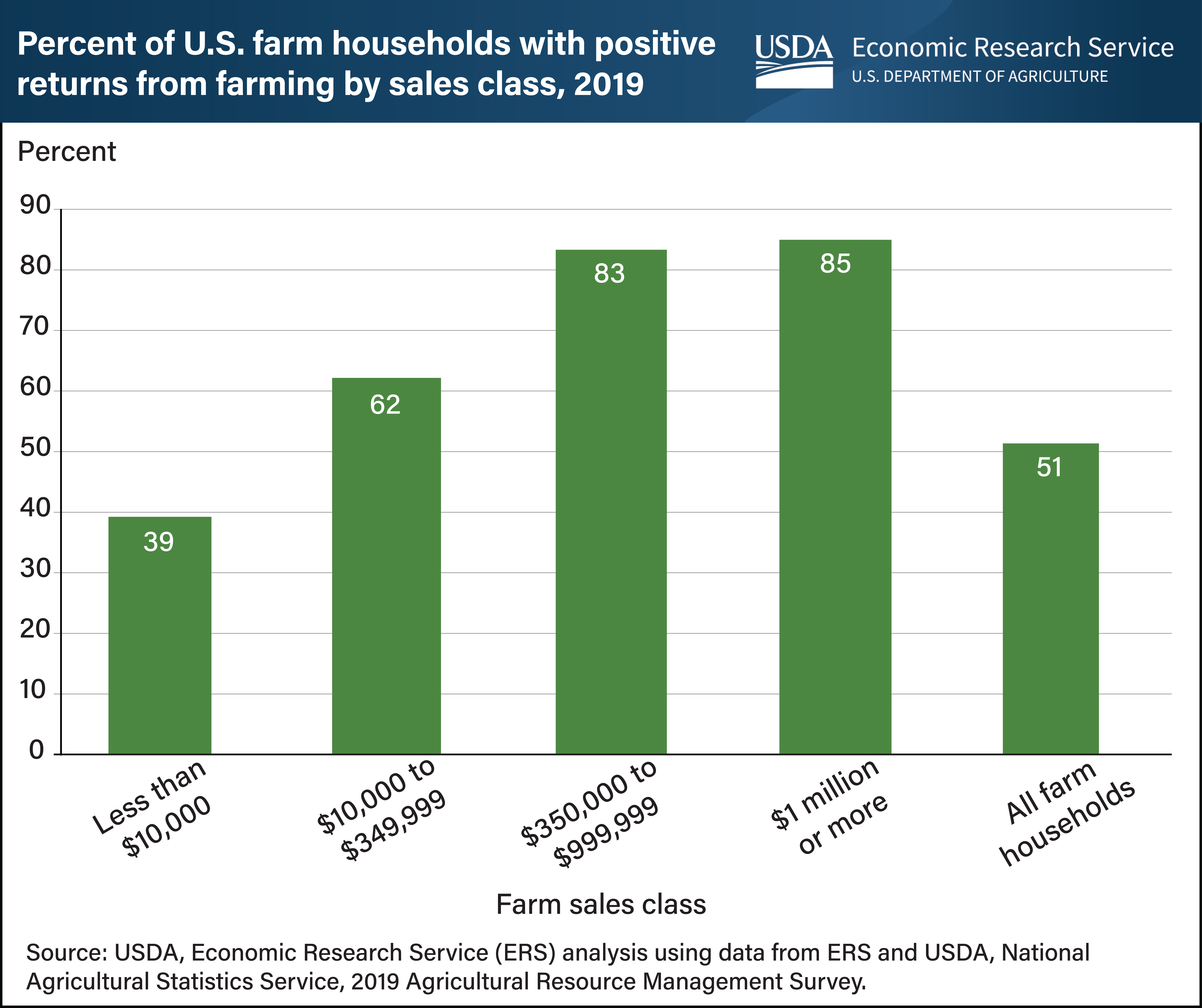
Farm households earn income from both farm operations and off-farm sources, such as off-farm employment, pensions, and capital gains. In 2019, more than half (51 percent) of all U.S. farm households had positive net returns, where total revenue from farming exceeded total costs. Farms with higher sales had a larger share of households with positive farm income. For example, 39 percent of farm households with annual gross sales less than $10,000 had positive farm income, compared with 85 percent of farms with sales of $1 million or more. At the same time, 56 percent of households operated the smallest farms with sales of less than $10,000, compared with 4 percent operating the largest ones with annual sales of $1 million or more. Households operating larger farms relied more on income from farming than households operating smaller farms. For instance, households that operated farms with sales of $1 million or more—and that had net positive returns—earned a median share of 87 percent of their income from farming. For those with sales less than $10,000, that median share was 5 percent. This chart is based on data from the ERS data product ARMS Farm Financial and Crop Production Practices, updated December 2020.

