Principal operator, spouse or both worked off the farm in half of U.S. family farm households in 2019
- by Christine Whitt and Anil K. Giri
- 3/5/2021
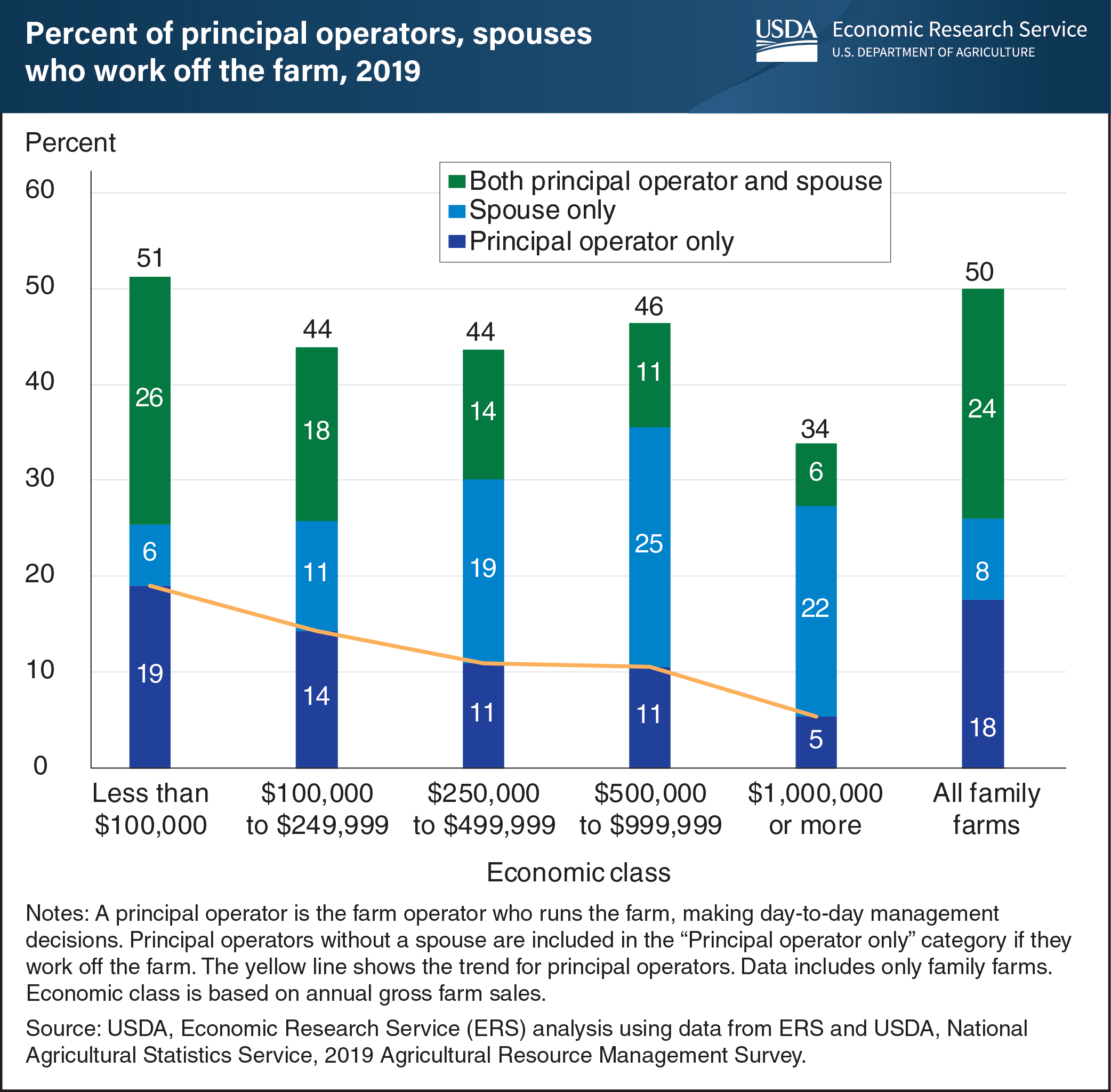
Farm households often rely on off-farm employment to provide other benefits, including health insurance, and to supplement their income. Loss of off-farm employment because of the COVID-19 pandemic can strain a farm household’s financial well-being. In 2019, 50 percent of all U.S. family farm households had the principal operator, the principal operator’s spouse, or both the principal operator and spouse working in an off-farm, wage-earning job. The shares of households working off-farm varied by the farm’s economic class. For small farms with less than $100,000 in annual gross farm sales, 51 percent had the principal operator, the spouse, or both work off the farm. By comparison, 34 percent of large farms with annual gross farm sales of $1 million or more had the principal operator, the spouse, or both work off the farm. As the farm’s sales size increases, the share of principal operators working off the farm decreased. Smaller family farms generally don’t earn enough from farm sources alone to cover household living expenses, whereas larger farms usually require increasingly more on-farm labor and management resources. While this information predates the COVID-19 pandemic, it can provide insights into the potential impact of decreased employment rates, which can result in the loss of off-farm employment for many farm households. This chart updates data found in the USDA, Economic Research Service report, America’s Diverse Family Farms, 2019 Edition, released December 2019.
See also: Farms and Farm Households During the COVID-19 Pandemic
We’d welcome your feedback!
Would you be willing to answer a few quick questions about your experience?

