Download chart image | Chart data
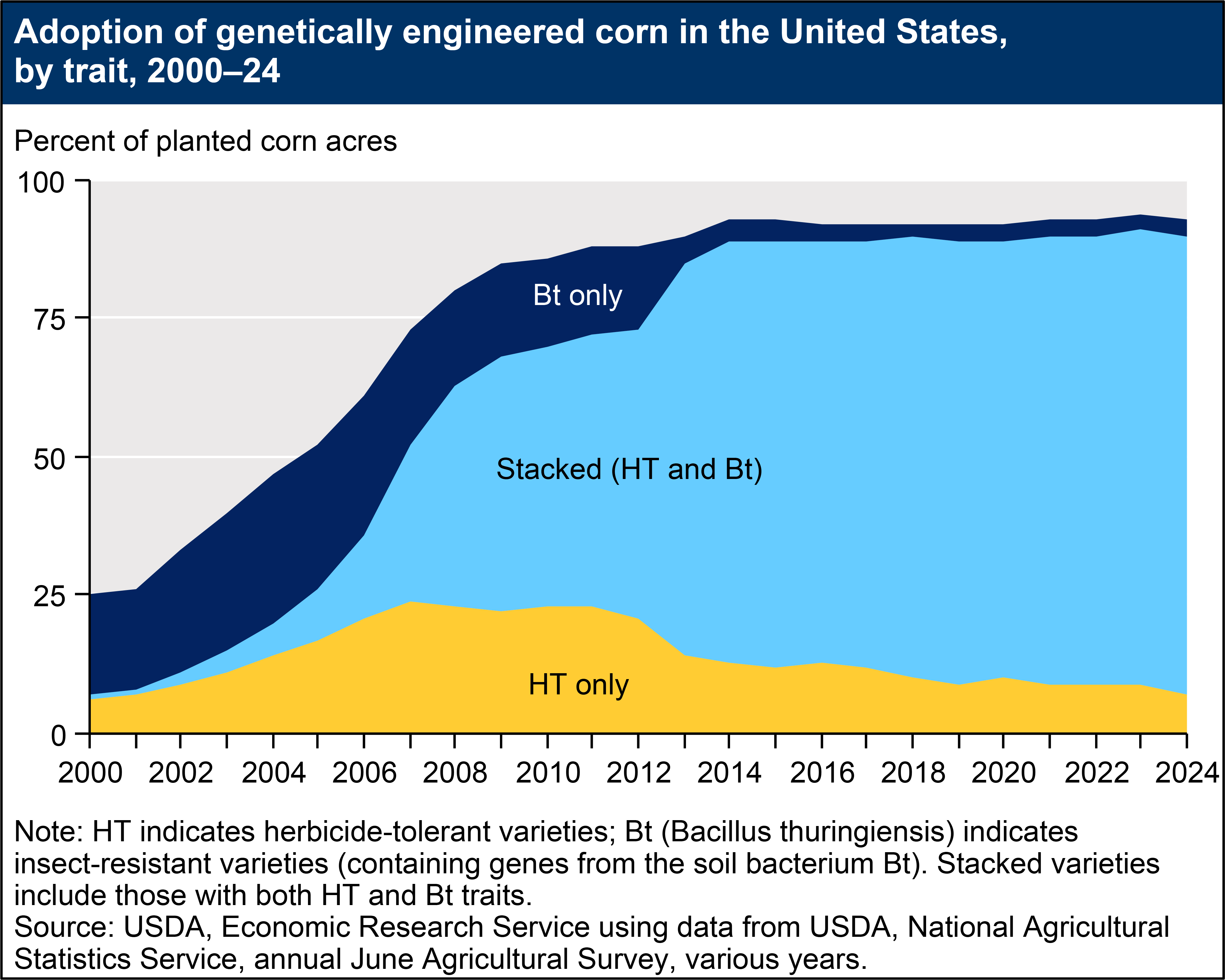
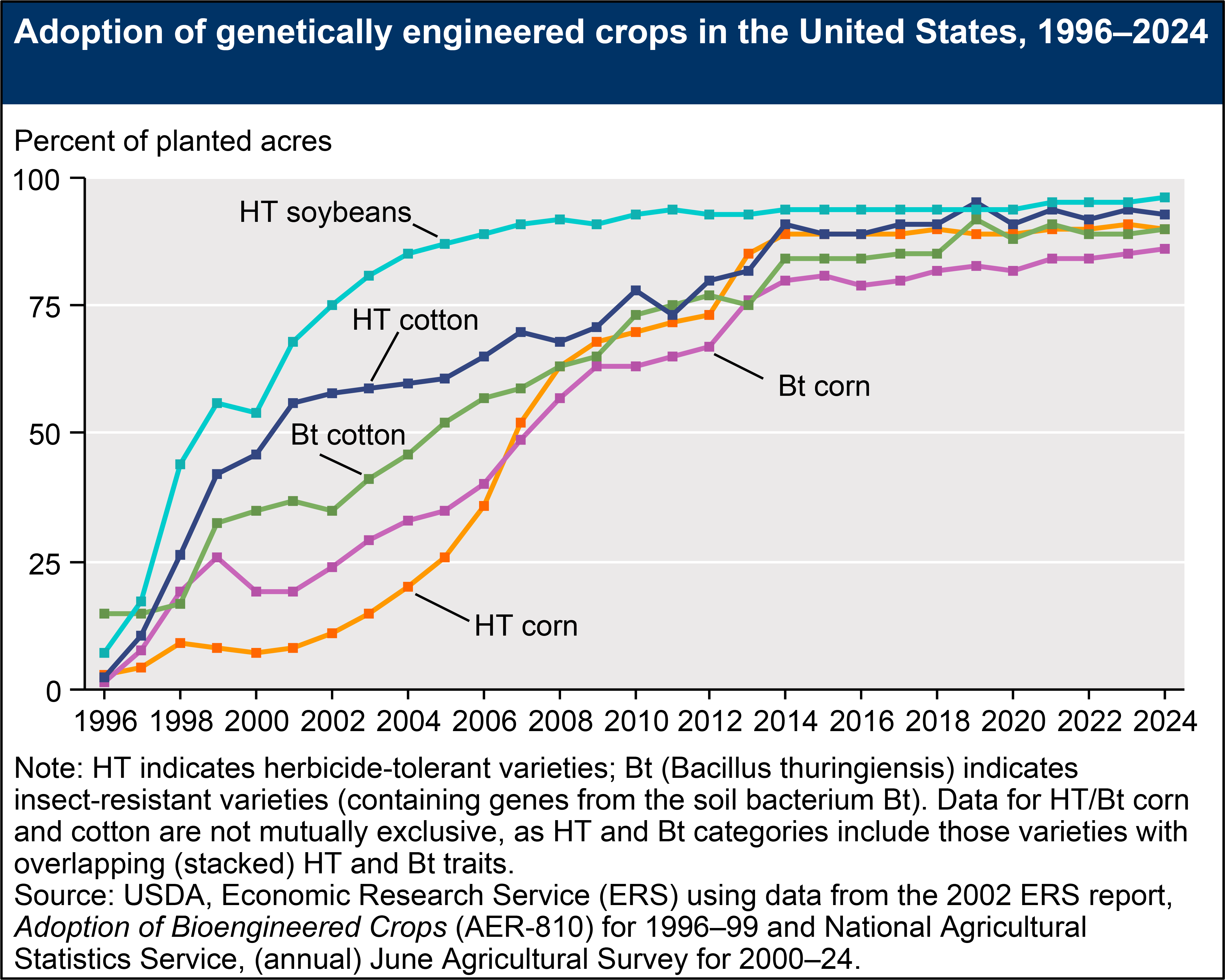
Genetically Engineered (GE) seeds were commercially introduced in the United States for major field crops in 1996, with adoption rates increasing in the years that followed. Currently, more than 90 percent of U.S. corn, upland cotton, and soybeans are produced using GE varieties. GE crops are broadly classified in this data product as herbicide-tolerant (HT), insect-resistant (Bt), or stacked varieties that are a combination of both HT and Bt traits. Although other GE traits have been developed (such as virus and fungus resistance, drought resistance, and enhanced protein, oil, or vitamin content), HT and Bt traits are the most used in U.S. crop production. Although HT seeds are also widely used in alfalfa, canola, and sugar beet production, most GE acres are planted to three major field crops: corn, cotton, and soybeans.
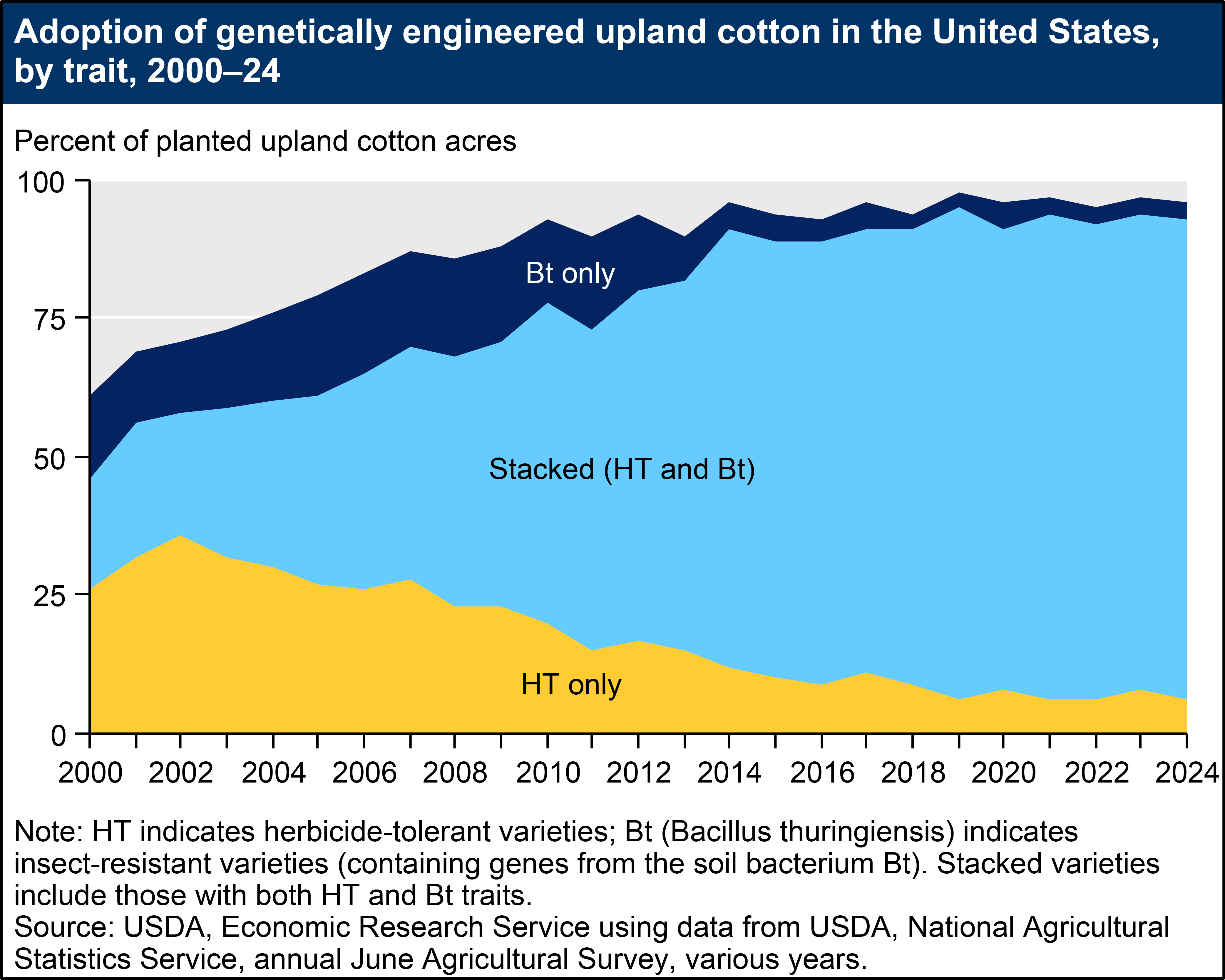
Herbicide-tolerant (HT) crops, which tolerate potent herbicides (such as glyphosate, glufosinate, and dicamba), provide farmers with a broad variety of options for effective weed control. Based on USDA survey data, the percent of domestic soybean acres planted with HT seeds rose from 17 percent in 1997 to 68 percent in 2001, before plateauing at 94 percent in 2014. In 2024, HT soybean acreage reached its highest adoption at 96 percent. HT cotton acreage expanded from approximately 10 percent in 1997 to 56 percent in 2001, before reaching a high of 95 percent in 2019. HT cotton acreage stood at 93 percent in 2024. Adoption rates for HT corn grew relatively slowly immediately following the commercialization of GE seeds. However, adoption rates increased following the turn of the century. In 2024, approximately 90 percent of domestic corn acres were planted with HT seeds.
Insect-resistant crops, which contain genes from the soil bacterium Bt (Bacillus thuringiensis) and produce insecticidal proteins, have been available for corn and cotton since 1996. Domestic Bt corn acreage grew from approximately 8 percent in 1997 to 19 percent in 2000, before climbing to 86 percent in 2024. Bt cotton acreage also expanded, from 15 percent of U.S. cotton acreage in 1997 to 37 percent in 2001. In 2024, 90 percent of U.S. cotton acres were planted with genetically engineered, insect-resistant seeds.
Increases in adoption rates for Bt corn may be due to the commercial introduction of new varieties resistant to the corn rootworm and the corn earworm (prior to 2003, Bt corn varieties only targeted the European corn borer). Adoption rates for Bt corn may fluctuate over time, depending on the severity of European corn borer and corn rootworm infestations. Similarly, adoption rates for Bt cotton may depend on the severity of tobacco budworm, bollworm, and pink bollworm infestations.
The figures below illustrate increases in adoption rates for stacked varieties, which have both (in some cases, multiple) HT and Bt traits. Adoption of stacked varieties has accelerated in recent years. Approximately 87 percent of cotton acres and 83 percent of corn acres were planted with stacked seeds in 2024.
Download chart image | Chart data