Agriculture's greenhouse gas emissions disproportionately high relative to share of economy
- by Carol Jones
- 6/2/2014
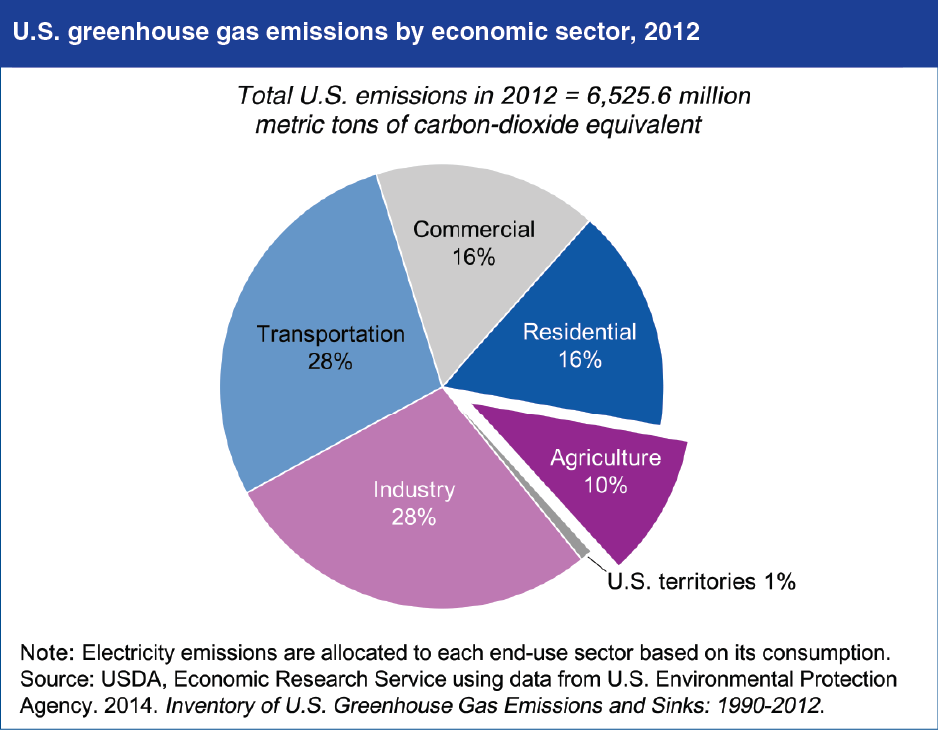
The agricultural sector accounted for about 10 percent of U.S. greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions in 2012. Given that agricultural production accounts for only about 1 percent of U.S. gross domestic product, it is a disproportionately GHG-intensive activity. In agriculture, crop and livestock activities are unique sources of nitrous oxide and methane emissions, notably from soil nutrient management, enteric fermentation (a digestive process in animals that produces methane), and manure management. GHG emissions from agriculture have increased by approximately 17 percent since 1990. During this time period, total U.S. GHG emissions increased approximately 5 percent. This chart is found in ERS’ Ag and Food Statistics: Charting the Essentials, updated May 2014.


