Growing share of older age population is living in high wildfire risk areas
- by Richelle L. Winkler
- 3/13/2025
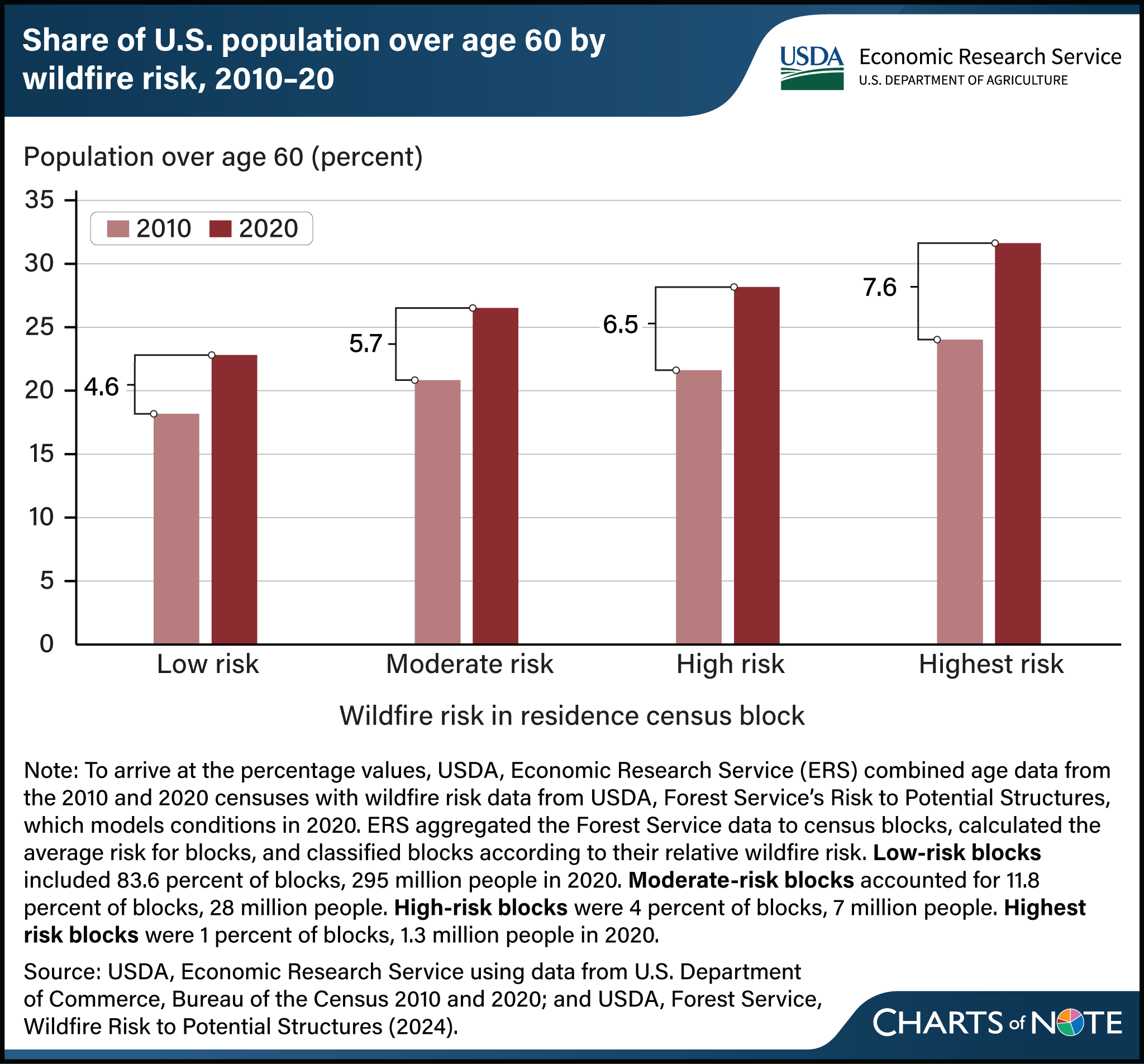
The population of the U.S. is aging. During the decade between the 2010 and 2020 censuses, the share of the population at older ages (over age 60) increased from 18.5 to 23.3 percent (4.8 percentage points). The older age share increased more in areas with greater wildfire risk. In areas of low wildfire risk, the share of the population age 60 or older increased 4.6 percentage points. The share of the population 60 or older increased 5.7 percentage points in areas with moderate wildfire risk, 6.5 points in areas with high risk, and 7.6 points in areas with the highest risk of wildfire. Nearly all (87 percent) of the 2010 to 2020 population growth in moderate, high, and highest wildfire risk areas was among people over age 60. Older people face a greater relative risk of dying in a fire than younger people and may require different support for wildfire risk mitigation, evacuation, and recovery. Aging population and wildfire risk both are more common in rural areas, so rural older populations are especially exposed to wildfire risk. This chart appears in the USDA, Economic Research Service report Aging and Wildfire Risk to Communities, published in February 2025.

