Prevalence of food insecurity in 2018 was down from 2017
- by Christian A. Gregory, Alisha Coleman-Jensen and Constance Newman
- 9/4/2019
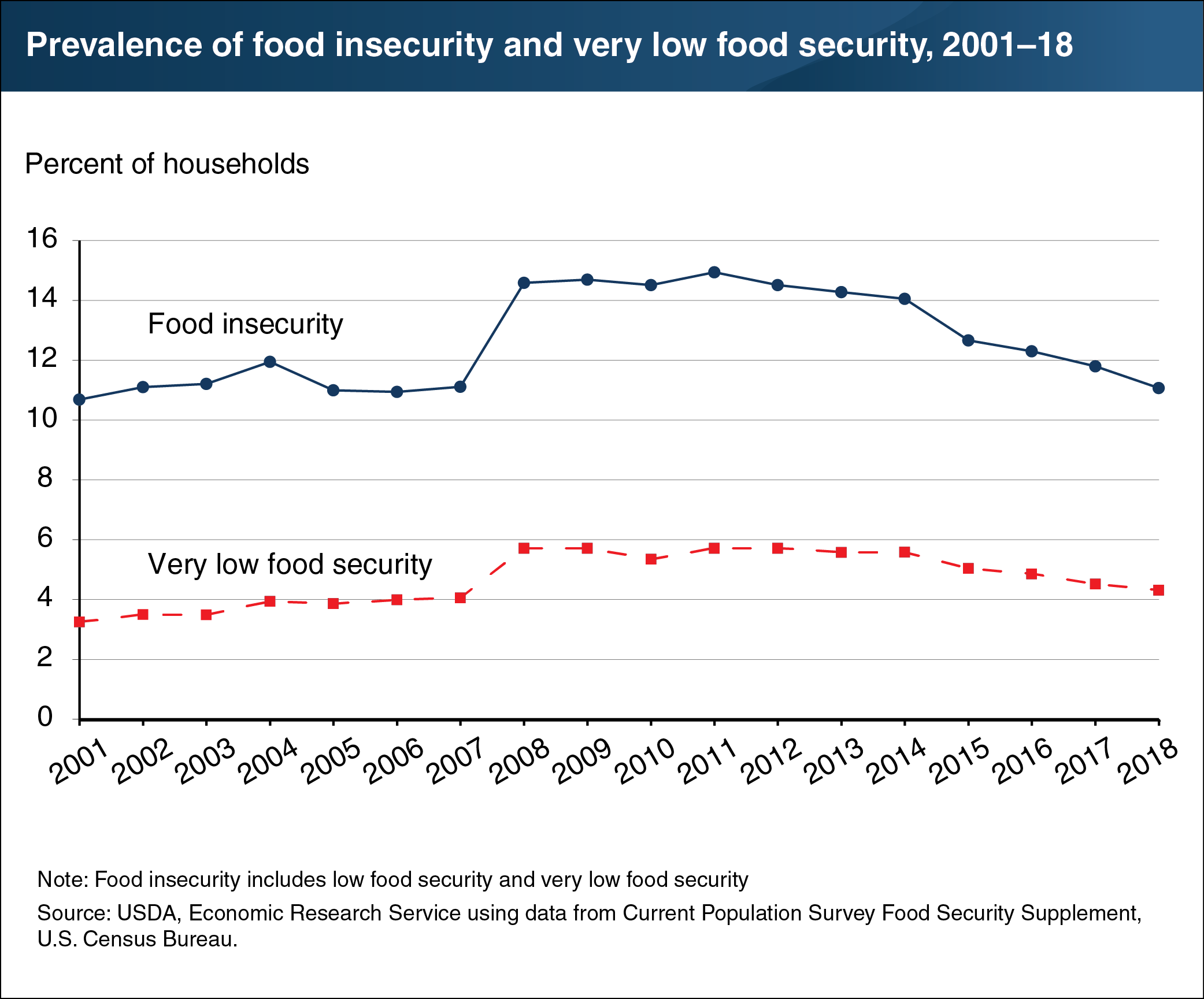
USDA’s Economic Research Service annually monitors the food security status of U.S. households. In 2018, an estimated 88.9 percent of U.S. households were food secure throughout the entire year, meaning they had access at all times to enough food for an active, healthy life for all household members. The remaining households (11.1 percent) were food insecure at least some time during the year, including 4.3 percent that experienced very low food security. In very-low-food-secure households, the food intake of one or more household members was reduced and their eating patterns were disrupted at times because the household lacked money and other resources for obtaining food. The prevalence of food insecurity overall declined from 11.8 percent in 2017. This change was statistically significant and continued a decline from a high of 14.9 percent in 2011. Very low food security was not significantly different from its 4.5-percent rate in 2017. This chart appears in the ERS report, Household Food Security in the United States in 2018, released September 4, 2019.


