Rural residents with higher educational attainment were more likely to engage in telehealth activities
- by Peter L. Stenberg
- 11/15/2018
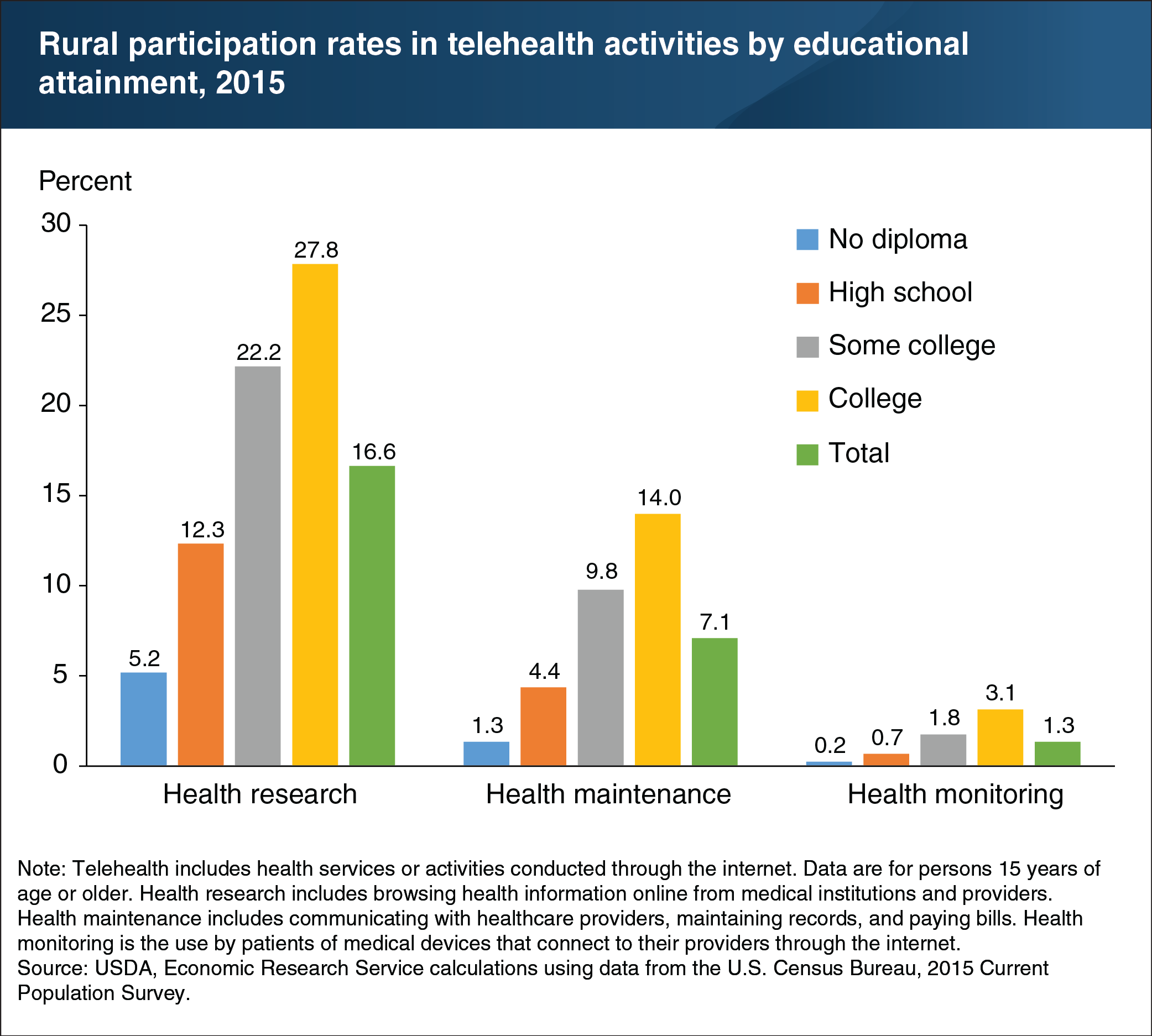
Compared to traditional medical delivery systems, telehealth—health services or activities conducted through the internet—allows people to more actively participate in their health care. It also facilitates timely and convenient monitoring of ongoing conditions. To better understand the factors affecting telehealth use, ERS researchers examined rural residents’ participation in three telehealth activities: online health research, online health maintenance (such as contacting providers, maintaining records, and paying bills), and online health monitoring (the transmission of data gathered by remote medical devices to medical personnel). The ERS analysis looked at a number of socioeconomic factors—including family income, educational attainment, age, and employment type and status—that may affect a person’s choice to engage in telehealth activities. Findings show that participation rates for telehealth activities in 2015 increased with the level of educational attainment. For example, rural residents with college degrees were over 5 times more likely to conduct online health research than residents without a high school diploma, and more than 10 times as likely to engage in the other telehealth activities. This chart appears in the November 2018 ERS report, Rural Individuals’ Telehealth Practices: An Overview.


