Prevalence of food insecurity varies across the country
- by Christian A. Gregory, Alisha Coleman-Jensen and Matthew P. Rabbitt
- 10/30/2018
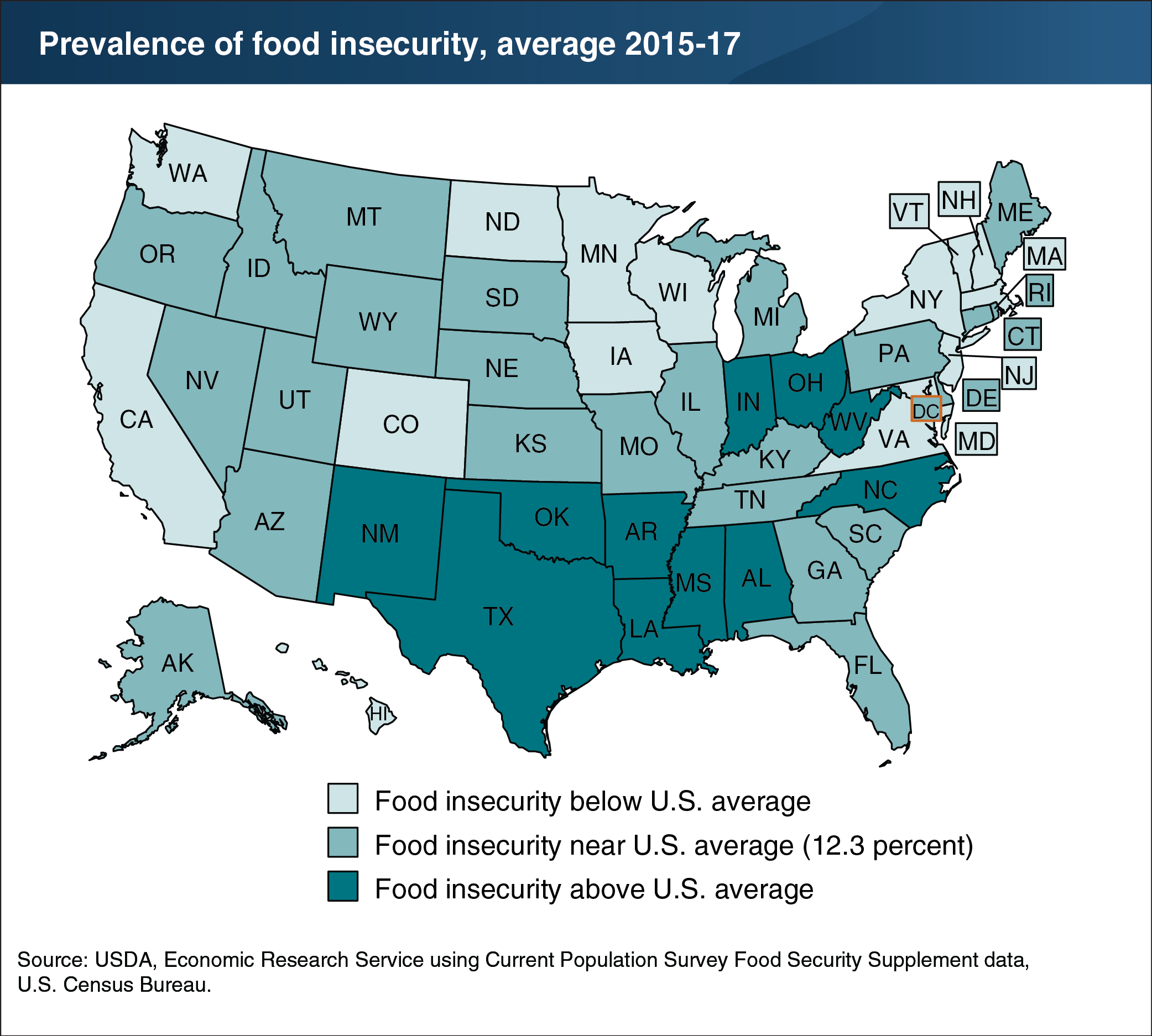
USDA monitors the extent of food insecurity in U.S. households at the national and State levels. Food-insecure households are defined as those that had difficulty at some time during the year providing enough food for all of their members due to a lack of resources. Food insecurity rates vary across States because of differing characteristics of the population, State-level policies, and economic conditions. The estimated prevalence of food insecurity during 2015-17 ranged from 7.4 percent of the population in Hawaii to 17.9 percent in New Mexico. Data for 2015-17 were combined to provide more reliable State statistics than 1 year alone would provide. In 11 States, the prevalence of food insecurity was higher than the 2015-17 national average of 12.3 percent, and in 15 States, it was lower than the national average. In the remaining 24 States and the District of Columbia, differences from the national average were not statistically significant. This map appears in ERS’s Ag and Food Statistics: Charting the Essentials.


