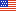
Southern States generally have a higher share of infants participating in WIC

USDA’s Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children (WIC) provides supplemental food, nutrition education, and referrals to health care and other social services to eligible low-income women, infants, and preschool children. In fiscal 2014, WIC served an average of 8.3 million people each month, including almost 2 million infants. State level data from fiscal 2012 reveal that on average, about 51 percent of all infants in the United States participated in the program. The share of infants that participated in the program varied by State, ranging from a low of 30 percent in Utah to a high of 67 percent in Mississippi. In six States (Mississippi, Arkansas, Kentucky, Louisiana, South Carolina, and Alabama)—all located in the southeastern United States—over 60 percent of all infants participated in WIC. Economic conditions impact both the percent of infants eligible to participate and the percent of eligible infants enrolled in the program. Participants in WIC must meet maximum income guidelines. A State with a more robust economy is more likely to have fewer residents who qualify for WIC. The statistics for this map can be found in the ERS report, The WIC Program: Background, Trends, and Economic Issues, 2015 Edition, January 2015.
Download higher resolution chart (1041 pixels by 832, 150 dpi)