In 2012, 91 percent of SNAP benefits went to households with incomes at or below the Federal poverty line
- by Laura Tiehen
- 7/28/2014
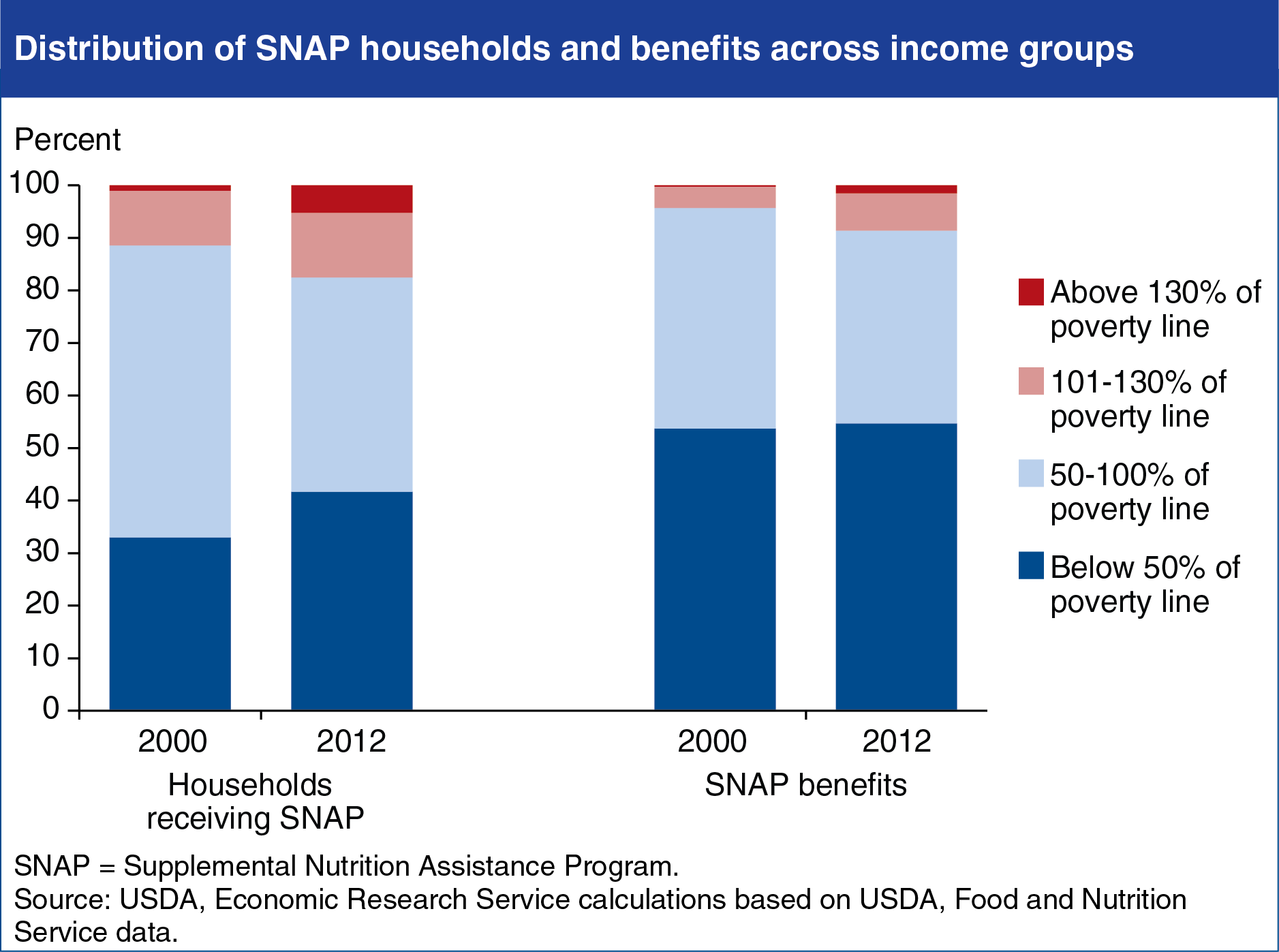
Federal eligibility rules for USDA’s Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP) stipulate that households must meet three financial criteria: gross income, net income, and asset limits. States using broad-based categorical eligibility criteria are allowed to eliminate the asset limit and increase the monthly gross income limit from 130 percent of the Federal poverty line up to 200 percent when determining SNAP eligibility. This new eligibility option is among the many legislative and regulatory efforts to simplify SNAP administration and increase program access, especially for low-income working families. During the discussions leading up to the Agricultural Act of 2014, concerns were raised that the broad-based categorical eligibility option had allowed assistance to expand beyond the poorest Americans. In 2012, 5.2 percent of SNAP households had incomes above 130 percent of the Federal poverty line—compared to 1.0 percent in 2000—and they received 1.5 percent of total SNAP benefits. This chart and a discussion of other SNAP-related provisions of the 2014 Farm Act can be found in “2014 Farm Act Maintains SNAP Eligibility Guidelines and Funds New Initiatives” in the July 2014 issue of ERS’s Amber Waves magazine.


