Farm sector profits projected to fall in 2023 after record highs in 2022
- by Farm Income Team
- 2/7/2023
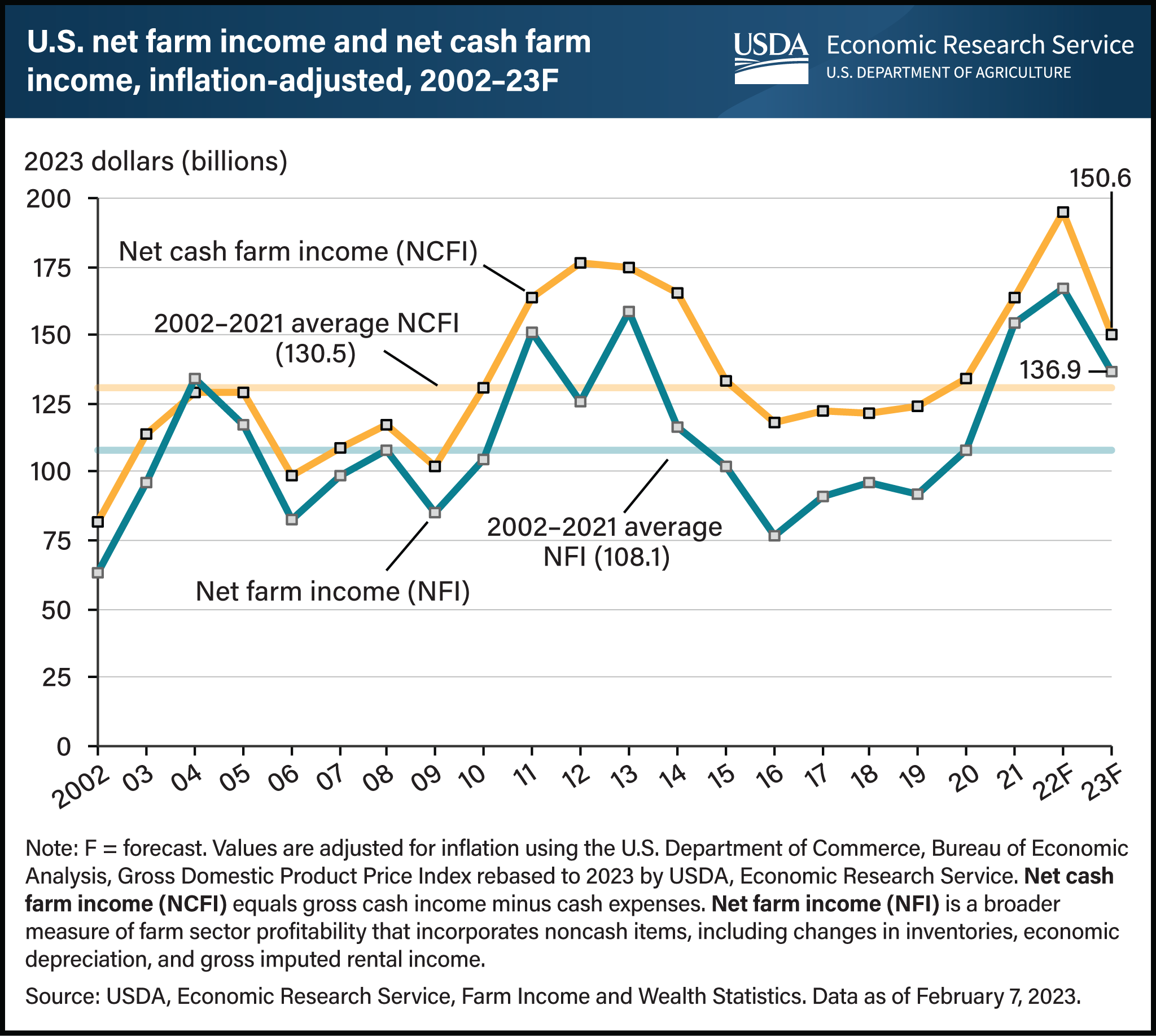
The USDA, Economic Research Service forecasts inflation-adjusted U.S. net cash farm income (NCFI)—gross cash income minus cash expenses—to decrease by $44.7 billion to $150.6 billion in 2023. This marks a 22.9 percent decline after reaching a forecast record high of $195.3 billion in 2022. U.S. net farm income (NFI) is forecast to decrease by $30.5 billion (18.2 percent) to $136.9 billion in 2023 after reaching a forecast of $167.3 billion in 2022, its highest level since 1973 after adjusting for inflation. (Calculations include rounding.) Net farm income is a broad measure of farm sector profitability that incorporates noncash items, including changes in inventories, economic depreciation, and gross imputed rental income. If these forecasts are realized, both NCFI and NFI would remain above their respective 20-year averages (2002–2021) in 2023. Underlying these forecasts, cash receipts for farm commodities are projected to fall by $38.9 billion (7.0 percent) from 2022 to $519.8 billion in 2023. During the same period, production expenses are expected to increase by $5.7 billion (1.3 percent) to $459.5 billion. Additionally, direct Government payments to farmers are projected to fall by $5.8 billion (36.2 percent) from 2022 levels to $10.2 billion in 2023, largely because of anticipated lower payments from supplemental and ad hoc disaster assistance programs. Find additional information and analysis on the USDA, Economic Research Service’s topic page Highlights from the Farm Income Forecast, reflecting data released on February 7, 2023.


