Rural young women show increases in higher educational attainment compared to rural young men
- by Brandon Genetin and Kelsey L. Thomas (Conley)
- 10/14/2022
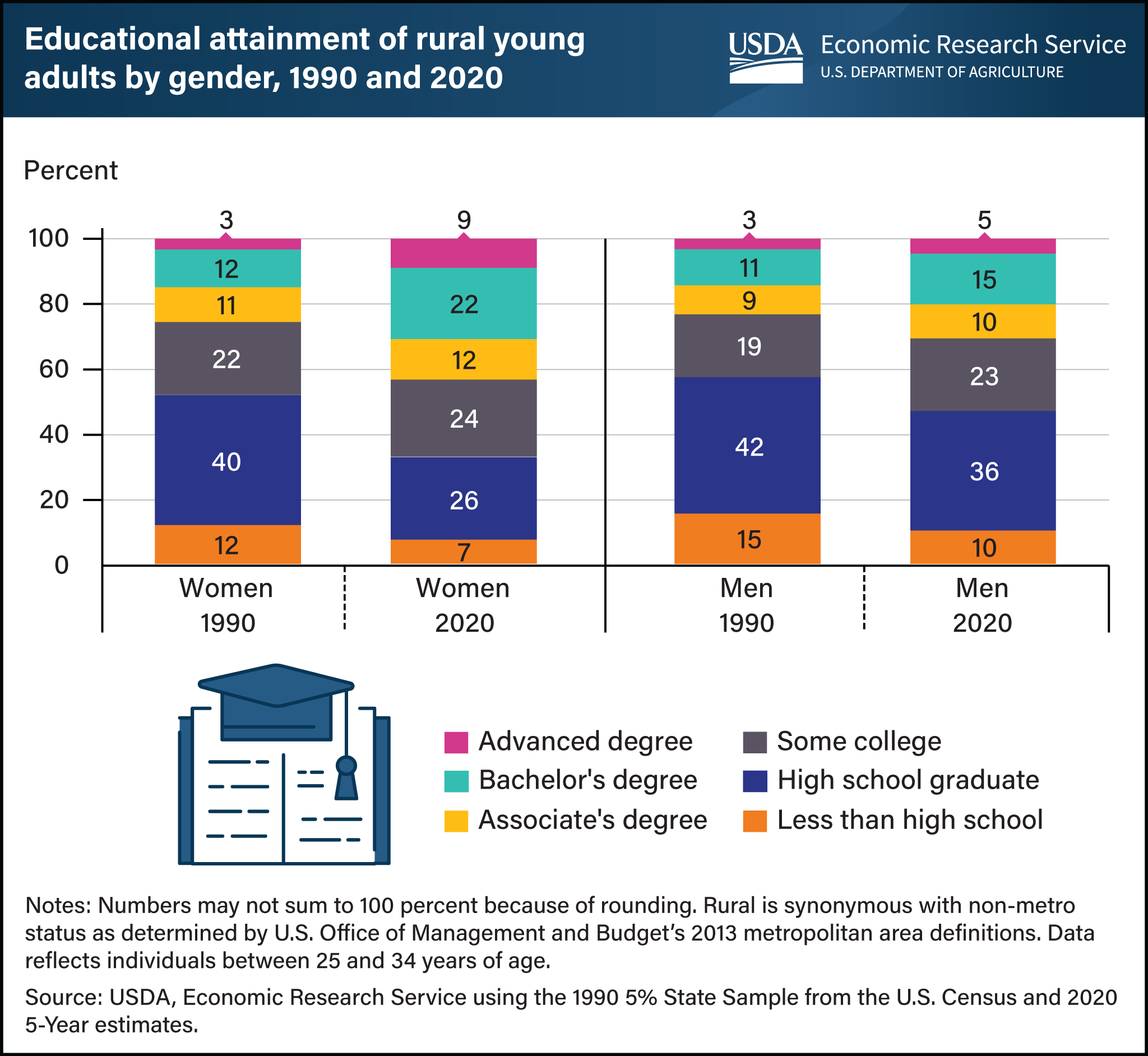
In rural areas, the level of educational attainment for women ages 25–34 continues to outpace young men. In 1990, 48 percent of rural young women had post-high school education, compared to 42 percent of rural young men. By 2020, this 6-percentage-point difference in post-high school educational attainment between the sexes increased to 14 percentage points, with 67 percent of rural, young women having post-high school education compared to 53 percent for their male counterparts. From 1990 to 2020, higher education rates for young, rural females increased almost 19 percentage points. The majority of that increase (10 percentage points) came from a rise in bachelor’s degrees, with another 6 percent coming from gains in advanced degrees, such as graduate or medical degrees. Educational attainment often has direct implications for earnings, with higher levels linked to increased wages and lower rates of unemployment, as discussed in Rural Education at a Glance, 2017 Edition. This is even more relevant for rural areas, where median earnings do not keep pace with urban area earnings. This chart updates information found in Rural Education at a Glance, 2017 Edition.


