Market Segments
USDA, Economic Research Service research on foodservice outlets— facilities that serve meals and snacks for immediate consumption on site (food away from home)—examines the size of this growing market and the major market segments, such as limited-service and full-service outlets.
A Large and Growing Market
The foodservice industry has been larger than food retailing since 2009:
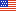
- The foodservice and food retailing industries supplied about $1.88 trillion worth of food in 2019.
- Of this total, $1.06 trillion was supplied by foodservice facilities. Full-service and limited-service establishments supplied about $400 million each.
However, in 2020 the foodservice industry had the sharpest decline in history (12.7 percent) partly as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic, mobility restrictions affecting food-away-from-home establishments, and the subsequent recession.
- In 2020, the foodservice and food retailing industries supplied about $1.81 trillion worth of food.
- Of this total, $925.3 billion was supplied by foodservice facilities. Full-service establisments supplied $272 billion and limited-service establishments supplied $349 billion.
In 2021 and 2022, the foodservice industry surpassed pre-pandemic levels.
- The foodservice and food retailing industries supplied about $2.11 trillion worth of food in 2021 and $2.39 trillion in 2022.
- Of this total, $1.16 trillion was supplied by foodservice facilities in 2021 and $1.34 trillion in 2022. In 2022, full-service establishments supplied $463 billion and limited-service establishments supplied $468 billion.
Commercial foodservice establishments accounted for the bulk of food-away-from-home expenditures. This category includes full-service restaurants, limited-service outlets, caterers, some cafeterias—and other places that prepare, serve, and sell food to the general public for a profit. Some establishments are located within facilities that are not primarily engaged in dispensing meals and snacks, such as lodging places, recreational facilities, and retail stores. Schools and nursing homes are types of non-commercial foodservice establishments, and such establishments are often called "institutional" foodservice facilities.
Download chart data in Excel file
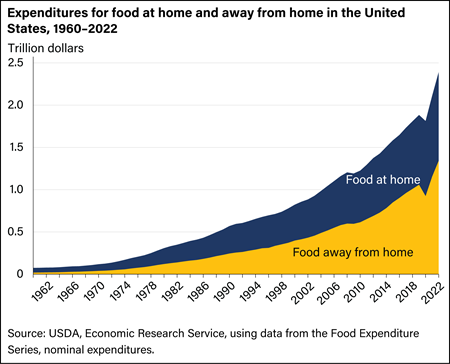
In 2022, the share of food-at-home expenditures was 43.8 percent, and food away from home was 56.2 percent—nearing the record high for the food-away-from-home expenditure share from 2019, after declining to 51.1 percent in 2020.
Download chart data in Excel format
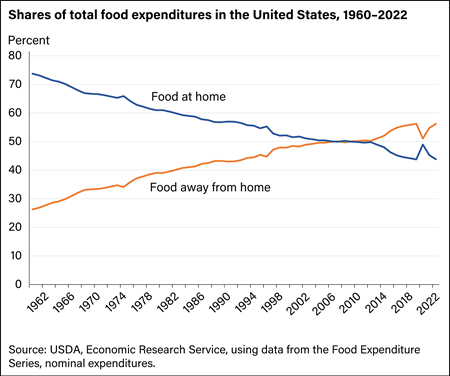
Full-service and limited-service restaurants—the two largest segments of the commercial foodservice market—accounted for about 69.3 percent of all food-away-from-home sales in 2022. Full-service establishments have wait staff, and likely other amenities such as nondisposable dishware and utensils, and alcohol service. In contrast, limited-service outlets use convenience as a selling point; they have no wait staff, menus tend to be limited, and dining amenities are relatively sparse. Given their limited physical interactions with customers, limited-service outlets were better able to adapt to COVID-19 restrictions during 2020. Full-service restaurants experienced the sharpest decline (24.2 percent) compared to limited-service outlets (3.0 percent) and all other food establishments (10.7 percent) in 2020. In 2022, all other foodservice establishments experienced the largest increase (19.5 percent) in sales compared to full-service restaurants (17.3 percent) and limited-service outlets (12.6 percent).
As part of their growth strategy, limited-service companies built more outlets closer to consumers' homes and work places to make it more convenient for consumers to purchase meals and snacks. Many limited-service restaurant companies opened outlets in nontraditional locations, such as department stores. In addition to convenience, a household's demand for food-away-from-home is affected by its income and demographic characteristics, as seen in the link below:
The Demand for Food Away from Home: Full-Service or Fast Food?Download chart data in Excel format
Any shift in the market share between limited-service and full-service restaurants could influence the mix of foods and services offered by both types of establishments. For example, if trends favor full-service restaurants, the market could shift to more full-service restaurants offering a wider range of menu selections and dining amenities. In response, limited-service outlets might introduce comparable foods and services.