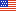
California’s olive processing industry shifts from canning to crushing

The turn of the century marked a shift in California’s olive industry. Historically, the State’s olive industry—which accounts for about 84 percent of olive acreage in the United States—was synonymous with canned olive production. Between 1980 and 2000, about 90 percent of California’s production was used for canned olives, most of which were of the black-ripe variety. California black-ripe olives are harvested green, before full maturity, and turn black from oxidation during processing. These shiny black-ripe olives are commonly sold as whole pitted or sliced canned products at retail or food service, where they often are used as pizza or salad toppings. Since the mid-2000s, the share of California’s olive production used to make olive oil has grown rapidly, from 10 percent in 2005 to more than 75 percent in 2022. This shift has been driven by increases in labor costs and import competition, as well as technological advancements that have made harvesting new olive oil-type cultivars comparatively quicker and less expensive. California olive oil production rose from 2 million pounds in 2006 to an average of 21 million pounds in 2021–23. Despite this increase in U.S. olive oil production, imports still supply more than 98 percent of the domestic consumption. This chart is based on the USDA, Economic Research Service Fruit and Tree Nuts Outlook Report, released March 2024.
Download larger size chart (2048 pixels by 1352, 96 dpi)