Food Prices and Spending
Retail food prices partially reflect farm-level commodity prices, but other costs of bringing food to the market (such as processing and retailing) have a greater role in determining prices on supermarket shelves and restaurant menus. Monthly price swings in grocery stores for individual food categories, as measured by the Consumer Price Index (CPI), tend to smooth out into modest yearly increases for food in general. In 2022, U.S. consumers, businesses, and government entities spent $2.39 trillion on food and beverages in grocery stores and at other retailers as well as on away-from-home meals and snacks.
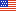
Average annual food-at-home prices were 5.0 percent higher in 2023 than in 2022. For context, the 20-year historical level of retail food price inflation is 2.5 percent per year. Price growth slowed in 2023 compared with 2022, when food-at-home prices rose by 11.4 percent. Prices for fats and oils rose the fastest in 2023 (9.0 percent), followed by sugar and sweets (8.7 percent), and cereals and bakery products (8.4 percent). Pork was the only category to decline in price in 2023, by 1.2 percent. Prices for several categories grew more slowly than their historical averages, including beef and veal (3.6 percent), eggs (1.4 percent), fresh vegetables (0.9 percent), fresh fruits (0.7 percent), and fish and seafood (0.3 percent).
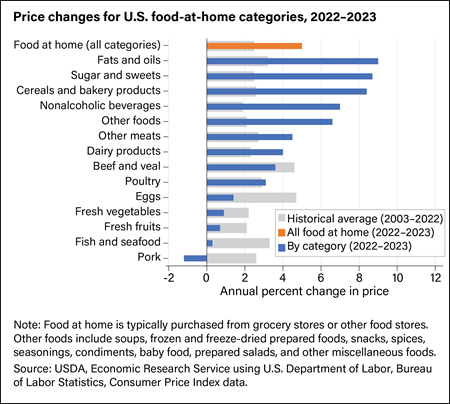
From 2019 to 2023, the all-food Consumer Price Index (CPI) rose by 25.0 percent—a higher increase than the all-items CPI, which grew 19.2 percent over the same period. Food price increases were below the 27.1-percent increase in transportation costs, but they rose faster than housing, medical care, and all other major categories. Food price increases in 2020–21 were largely driven by shifting consumption patterns and supply chain disruptions resulting from the Coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic. In 2022, food prices increased faster than any year since 1979, partly due to a highly pathogenic avian influenza outbreak that affected egg and poultry prices and the conflict in Ukraine which compounded other economy-wide inflationary pressures such as high energy costs. Food price growth slowed in 2023 as wholesale food prices and these other inflationary factors eased from 2022.
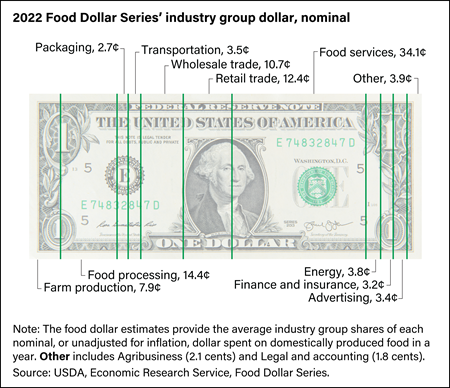
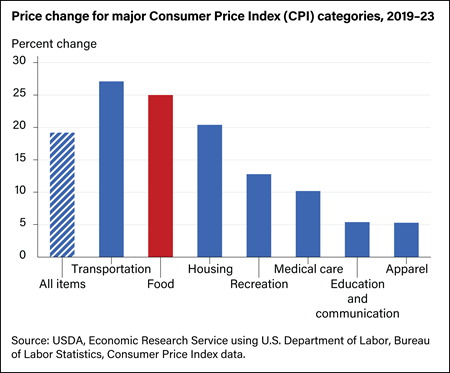
For a typical dollar spent in 2022 by U.S. consumers on domestically produced food, including both grocery store and eating-out purchases, 34.1 cents went to foodservice establishments such as restaurants and other eating-out places. For the remainder of the food dollar, retail trade (12.4 cents) decreased to its lowest share since 1995 and wholesale trade (10.7 cents) decreased to its lowest share since 2011. Food processing (14.4 cents) also decreased to its lowest share since at least 1993, the first year recorded in the series.
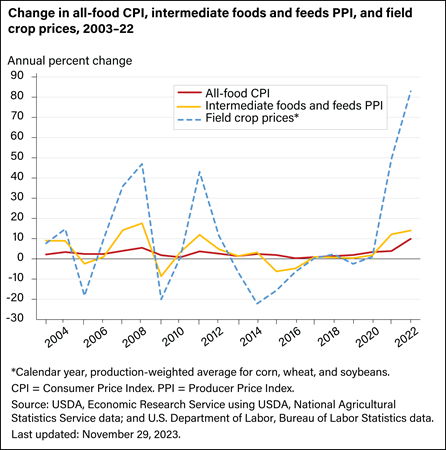
Corn, wheat, and soybeans are the top three U.S. field crops and comprise the majority of field crop inputs to the U.S. food supply. The average farm price of these crops, weighted by total production, regularly rises or falls by more than 10 percent from one year to the next. However, these price swings have relatively small impacts on food prices. In 2022, the production-weighted price of these crops increased by 83 percent, while food prices increased by 10 percent. Intermediate foods and feeds price fluctuations generally range between swings in field crop and food prices.
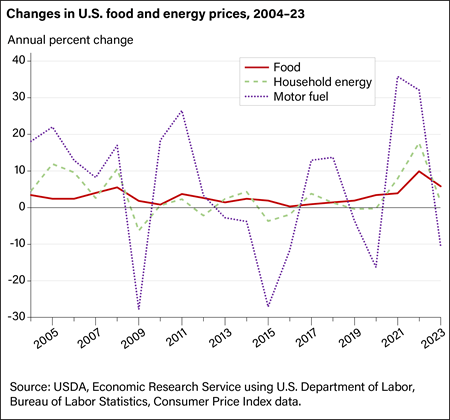
Food and fuel prices are typically more volatile than other consumer spending categories, but the price swings differ in size. Over the past two decades, motor fuel prices often experienced double-digit annual price swings, and the average annual change in food prices (3.0 percent) was lower than household energy (3.3 percent) and motor fuel prices (5.9 percent). In 2023, food prices grew by 5.8 percent, while household energy prices increased by 1.6 percent and motor fuel prices declined by 10.6 percent following relatively large increases for each of these categories in 2022.
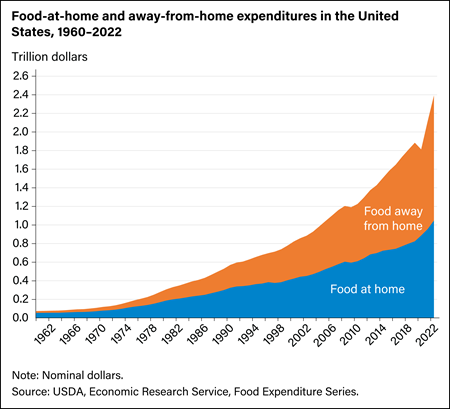
In 2022, food spending by U.S. consumers, businesses, and government entities totaled $2.39 trillion, after a sharp decline in 2020 in which the food market was disrupted by the Coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic and the recession. U.S. food spending in 2020 totaled $1.81 trillion. Food-at-home spending increased from $954.7 billion in 2021 to $1.05 trillion in 2022 and food-away-from-home spending increased from $1.16 trillion in 2021 to $1.34 trillion in 2022. Food-away-from-home spending accounted for 56 percent of total food expenditures in 2022.
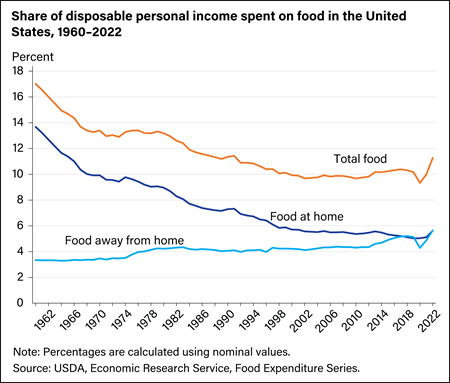
U.S. consumers spent an average of 11.3 percent of their disposable personal income on food in 2022— reaching levels similar to the 1980s. The share of disposable personal income spent on food in 2022 was divided nearly equally between food at home (5.62 percent) and food away from home (5.64 percent). The share of disposable personal income spent on total food has trended downward—driven by a decline in share of income spent on food at home. In 2020, during the Coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic, the share of disposable income spent on total food presented the sharpest annual decline (8.2 percent) since 1967. In 2022, the share of disposable personal income spent on total food had the sharpest annual increase (12.7 percent)—driven by an increase in the share of income spent on food away from home.
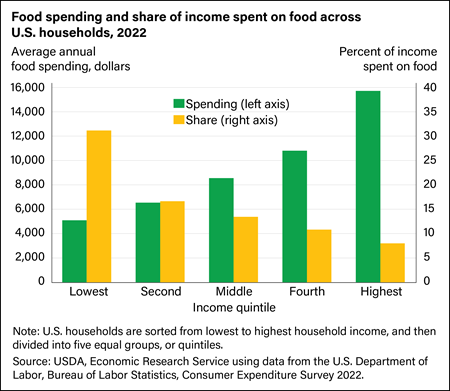
As their incomes rise, U.S. households spend more money on food but it represents a smaller share of their income. In 2022, households in the lowest income quintile spent an average of $5,090 on food (representing 31.2 percent of income), while households in the highest income quintile spent an average of $15,713 on food (representing 8.0 percent of income).
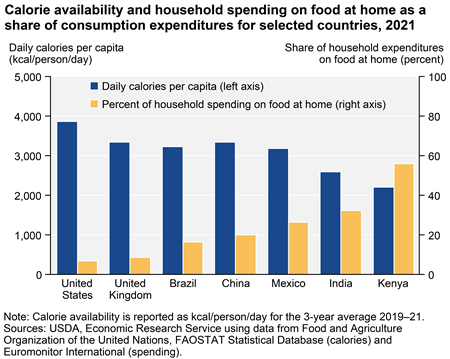
High-income countries such as the United States and the United Kingdom have higher food spending in absolute terms, but the share of household consumption expenditures devoted to at-home food is low—less than 10 percent. In Kenya and other low-income countries, at-home food’s share of consumption expenditures can exceed 50 percent. Per capita calorie availability follows the reverse pattern. According to the most recent available data, U.S. per capita calorie availability was among the highest at 3,864 calories per person per day, while Kenya’s was estimated at 2,201 calories per person per day.